Jump-starting a car is a common solution when you find yourself with a dead battery. However, what you do immediately after the jump-start is crucial to ensure that your battery recharges and your car remains operational. So, how long to leave car on after jump start?
I will help you understand how long to leave your car running after a jump start and why it’s important for your vehicle’s battery health. Understand the process and precautions when jump-starting a 24V system with a 12V battery to prevent system overloads.
Why Should You Leave the Car On After a Jump Start?
Jump-starting a car only provides a temporary boost to your dead battery. The primary goal afterward is to recharge the battery so it has enough power to restart your car without external assistance. The alternator in your vehicle is responsible for recharging the battery while the engine is running.
If you do not allow the car to run for a sufficient amount of time after the jump start, the battery might not recharge fully, leading to a recurring need for jump-starts. In addition, insufficient charging puts extra stress on your alternator, potentially causing damage and shortening its lifespan.
How Long to Leave Car On After Jump Start?
So, how long to leave car on after jump start? Experts generally recommend that you drive the car for at least 20 to 30 minutes after a jump start. This allows the alternator to provide a sufficient charge to the battery.
Ideally, you should drive the car rather than leave it idling, as driving at highway speeds allows the alternator to work more efficiently compared to idling (which may take much longer to charge the battery fully). Explore the best portable marine battery jump starters for reliable performance when you’re out on the water.
In cases where it is not possible to drive the car, letting it idle for at least 30 minutes is still beneficial, but not as effective as driving. If the battery does not hold the charge after running for this duration, it may be a sign of an underlying issue, such as a weak battery or a faulty alternator.
Factors That Affect Charging Time
- Battery Condition: If your battery is old or has been discharged for a long time, it might take longer to fully recharge. In some cases, a weak battery may require several hours or overnight to reach full capacity.
- Driving Conditions: Driving at a constant speed on highways helps recharge the battery faster compared to city driving with frequent stops and starts.
- Alternator Health: If your alternator is not functioning properly, it may struggle to recharge the battery, leading to potential issues with starting the car later on.
Risks of Not Running the Car Long Enough
Failing to run your car for a sufficient amount of time after a jump start can lead to several issues:
- Recurring Dead Battery: The battery might not receive enough charge to start the car again, leading to repeated jump starts.
- Alternator Damage: The alternator may become overworked as it tries to compensate for a weak or uncharged battery, leading to premature failure.
- Risk of Stalling: Without enough charge, your car may stall during driving, which could be dangerous in certain situations.
Best Practices After Jump Starting
- Drive the Car: Driving is the best way to recharge the battery. Aim to drive at highway speeds for at least 20 to 30 minutes.
- Avoid Excessive Idling: While idling can recharge the battery, it is far less efficient than driving. The alternator generates more power when the car is being driven at higher speeds.
- Monitor Battery Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery’s voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts when the car is off and between 13.7 to 14.7 volts while the car is running.
- Check the Battery and Alternator: If your car requires frequent jump-starts, have a mechanic inspect the battery and alternator. This can help determine whether either component needs replacement.
Signs of a Dying Battery
Recognizing the signs of a weak battery can help you address issues before they lead to repeated jump-starts:
- Slow Engine Crank: If the engine takes longer than usual to turn over, it may be due to a weak battery.
- Dim Headlights: Dimming lights can indicate a lack of battery power.
- Weird Smell: A sulfuric smell could indicate a leaking battery.
- Swollen Battery Case: This could be a sign of overheating, which may require immediate attention.
Find out which portable car jump starter with air compressor is perfect for emergency roadside assistance.
Long-Term Maintenance Tips
- Regular Battery Checks: Inspect the battery terminals for corrosion and ensure that connections are tight.
- Minimize Electrical Usage: After a jump start, avoid using too many electrical components, such as air conditioning or heated seats, to allow the alternator to focus on charging the battery.
- Battery Replacement: If your battery frequently needs to be jump-started, it may be time to replace it. Depending on the type, a new battery can cost between $50 and $500.
Additional Steps to Ensure Proper Battery Charging
After a successful jump start, ensuring the battery is fully recharged is essential for the overall health of your vehicle. Here are some detailed steps you can take to enhance the charging process and prevent future issues.
1. Driving vs. Idling: What’s Better?
One of the most effective ways to recharge the battery after a jump start is to drive the car rather than leaving it idling. Driving at highway speeds helps the alternator generate maximum power, allowing the battery to charge faster.

If you let the car idle, it may take significantly longer to bring the battery up to a full charge due to the lower RPMs of the engine, which in turn results in less power output from the alternator.
In an ideal situation, drive your car for 20 to 30 minutes to recharge the battery effectively. During this time, try to maintain a steady speed and avoid frequent stops, which can interrupt the charging process.
2. Monitor Electrical Demand During Initial Charging
After jump-starting your car, you should minimize the use of electrical components like air conditioning, heated seats, infotainment systems, or other accessories that put additional load on the electrical system. This helps ensure that the maximum amount of power from the alternator is being used to recharge the battery, instead of being diverted to run these other systems (source: Ran When Parked).

3. Battery Voltage Monitoring
One of the best ways to determine if your battery is charging properly after a jump start is to monitor the battery voltage.
A battery voltage of around 12.6 volts indicates that the battery is fully charged when the car is off, and a reading between 13.7 to 14.7 volts while the engine is running indicates that the alternator is recharging the battery effectively (source: FuelFlowPro).
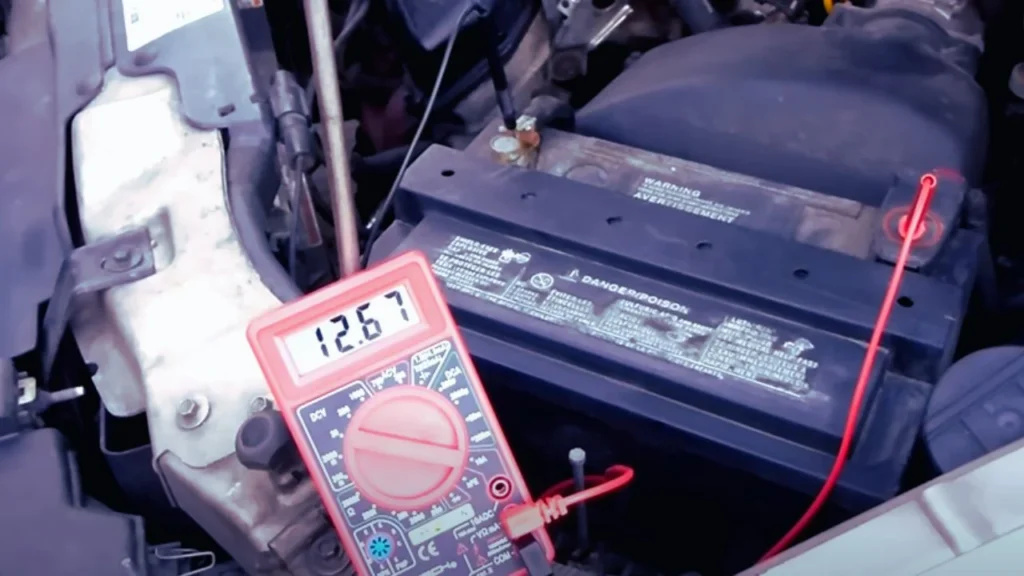
You can use a multimeter to check the voltage of your battery at various stages—right after a jump start, after 30 minutes of driving, and once you reach your destination. This can help you determine whether the battery is being adequately recharged.
This comprehensive guide on using a jump starter to charge a dead battery explains whether it’s possible and what to watch out for.
4. Checking the Alternator
After a jump start, if the car struggles to start again even after being driven for 30 minutes, it could indicate an issue with the alternator. The alternator is the component responsible for maintaining the battery charge while the engine is running. If the alternator is failing, it will not provide enough charge to the battery, leading to repeated stalls or the need for frequent jump starts.
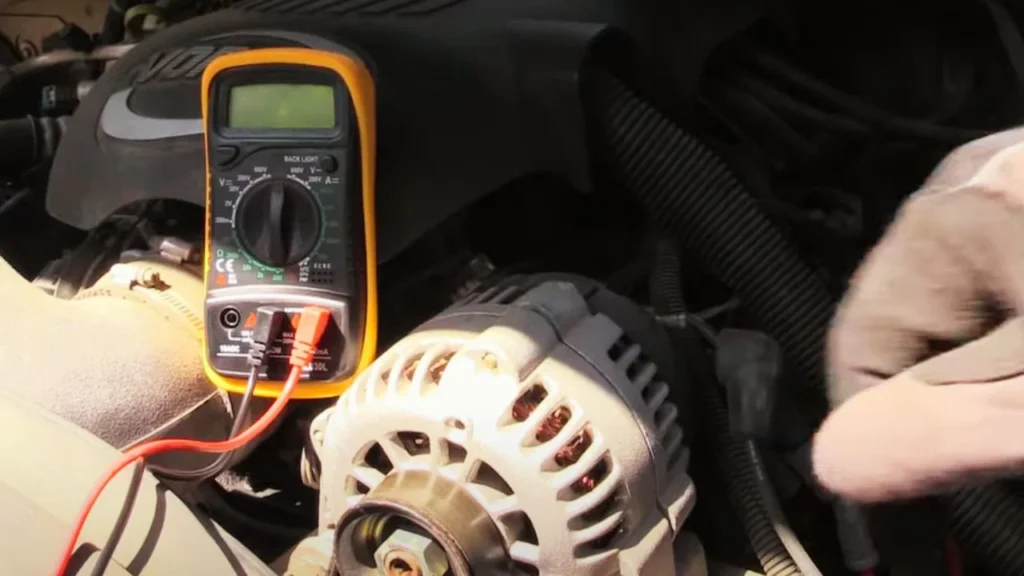

Signs of a failing alternator include:
- Dashboard Battery Light: If the battery warning light on your dashboard is on, it could indicate an issue with the charging system.
- Dimming Lights: Dimming of headlights, interior lights, or other electrical components can indicate that the alternator isn’t producing sufficient power.
If these signs are present, it’s best to have the alternator inspected and tested by a mechanic.
Preventing Future Battery Issues
A jump start is often a sign that the battery is either not holding a charge or that there is some other underlying issue. To avoid having to jump-start the car again, here are some preventive measures to consider:
1. Inspect Battery and Terminals Regularly
Corrosion on battery terminals can significantly reduce the effectiveness of charging and starting. Inspect the terminals for any signs of white, blue, or green buildup, and clean them regularly using a baking soda and water solution and a wire brush (source: Ran When Parked). Keeping the terminals clean ensures proper electrical contact.

Applying petroleum jelly or terminal grease after cleaning can also help prevent further corrosion and ensure a good connection.
2. Battery Maintenance
Regular battery maintenance can extend its lifespan. If your battery is not sealed, periodically check the water level in each cell. The level should cover the lead plates inside the battery. If the water level is low, use distilled water to top it up but avoid overfilling, as this can lead to acid leakage.

3. Charge the Battery Manually
If your car has been sitting for an extended period, the battery may lose charge. Using a battery maintainer or trickle charger can help keep the battery charged when the car is not in use. This is particularly useful during winter months when batteries are prone to losing charge due to the cold. Discover practical advice on how to jumpstart a refrigerator compressor, a useful guide for when your fridge stops cooling properly.

Risks of Not Running Your Car Long Enough
If you fail to run your car for a sufficient period after a jump start, several issues can arise:
- Recurring Battery Failure: Without enough time to recharge, the battery may fail again shortly after. This will leave you in need of another jump start, potentially at an inconvenient time.
- Alternator Stress: The alternator works extra hard to charge a completely dead battery. If the battery is not adequately recharged and keeps running out of power, this increased workload can lead to premature alternator failure, a repair that can be quite expensive.
- Vehicle Stalling: A partially charged battery may cause the car to stall during driving, especially if there’s a high electrical demand (like during nighttime driving with headlights on or during heavy use of HVAC systems).
Conclusion
Jump-starting your car is just the first step; what you do afterward is equally important. Leaving your car on for 20 to 30 minutes, preferably by driving, ensures that the battery is sufficiently recharged and ready for the next use. Failing to run your car for the appropriate amount of time could lead to recurring issues and potential damage to both your battery and alternator.
By following the recommendations provided and keeping an eye on your battery’s health, you can prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend the life of your vehicle’s electrical system. Hope so, now you know how long to leave car on after jump start. Explore whether it is bad to keep jump-starting your car battery, including the long-term effects it may have on your vehicle’s performance.
Ali is a tech enthusiast and automotive aficionado, passionate about sharing insights on the latest innovations and industry trends.





