Jump starters are an essential tool for many drivers, providing the power necessary to get a car battery up and running in an emergency. However, like any other battery-powered device, a jump starter has a limited lifespan. So, how long do jump starters last?

This guide will take you through the average lifespan of jump starters, the factors that affect their longevity, and how to maintain them to ensure they last as long as possible. Learn how to safely jump-start a box truck with this guide on jump-starting a box truck, covering essential tools and step-by-step instructions.
How Long Do Jump Starters Last | The Average Lifespan of a Jump Starter
So, how long do jump starters last? The typical lifespan of a jump starter varies depending on the battery type, maintenance, and usage patterns. On average, a well-maintained jump starter can last between 3 to 6 years. High-end models, especially those with lithium-ion batteries, may last even longer, reaching up to 10 years if properly cared for.
For example, lithium-ion jump starters are rated for 300 to 500 charge cycles, meaning you can charge them fully that many times before their capacity starts to degrade by about 20%. This degradation does not mean that the jump starter will completely stop working, but its ability to start a vehicle may decrease over time as its peak current diminishes. Here’s the breakthrough:
On the lower end of the spectrum, cheaper jump starters, particularly those using older lead-acid batteries, may only last around 3 years under typical conditions. Discover the steps for jump-starting a Mini Cooper efficiently and avoid damaging your car’s sensitive electronics.
Key Factors That Affect the Lifespan of a Jump Starter
The longevity of a jump starter depends on several factors, from how it’s used to how it’s stored. Here are the primary factors that influence its lifespan:

1. Battery Type
Lithium-ion batteries are generally the longest-lasting, providing between 5-10 years of use depending on how frequently they are used and charged. These batteries have a high energy density and are lightweight, which makes them ideal for portable jump starters.
Lead-acid batteries, on the other hand, tend to have shorter lifespans, averaging 3 to 5 years. They are bulkier and heavier, and their ability to hold a charge diminishes faster compared to lithium-ion batteries.

2. Frequency of Use
Using a jump starter frequently can affect how long it lasts. Typically, a jump starter is designed to be used 10 to 20 times per charge before it needs to be recharged. However, using the jump starter on a daily or weekly basis can wear out the internal battery more quickly than occasional use.

3. Storage Conditions
Temperature plays a significant role in battery health. Jump starters stored in environments that experience extreme heat or cold tend to degrade faster. Ideally, jump starters should be stored in environments where the temperature is between 50°F and 90°F. Anything outside this range can cause the internal battery to degrade more quickly.

4. Charging Habits
Proper charging is crucial to prolonging a jump starter’s lifespan. Most manufacturers recommend charging a jump starter at least every 3 to 6 months, even if it hasn’t been used. Allowing the battery to fully discharge can lead to permanent damage, especially with lithium-ion models.

On the flip side, overcharging the device can also reduce its lifespan. Many modern jump starters have built-in overcharge protection, but it’s still best to unplug the device once it’s fully charged.
5. Depth of Discharge
Another critical factor is how deeply the battery is discharged during use. Regularly discharging a jump starter to 0% before recharging it can significantly reduce its lifespan. Ideally, you should aim to recharge the jump starter when it falls below 20-30% capacity.

6. Maintenance
Maintenance can significantly impact how long a jump starter lasts. Simple practices like cleaning the connectors, keeping the device in a stable, cool environment, and regularly checking its charge level can all help extend its life. Understand the process and precautions when jump-starting a 24V system with a 12V battery to prevent system overloads.

Battery Type Breakdown: Lithium-Ion vs. Lead-Acid
Explore the key differences between Lithium-Ion and Lead-Acid batteries. This guide covers efficiency, lifespan, cost, and applications to help you choose the right battery for your needs.

1. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in modern jump starters due to their high energy density, lightweight design, and longer lifespan. These batteries are designed to handle 300 to 500 charge cycles, meaning they can be charged fully and depleted that many times before their performance degrades by about 20%.
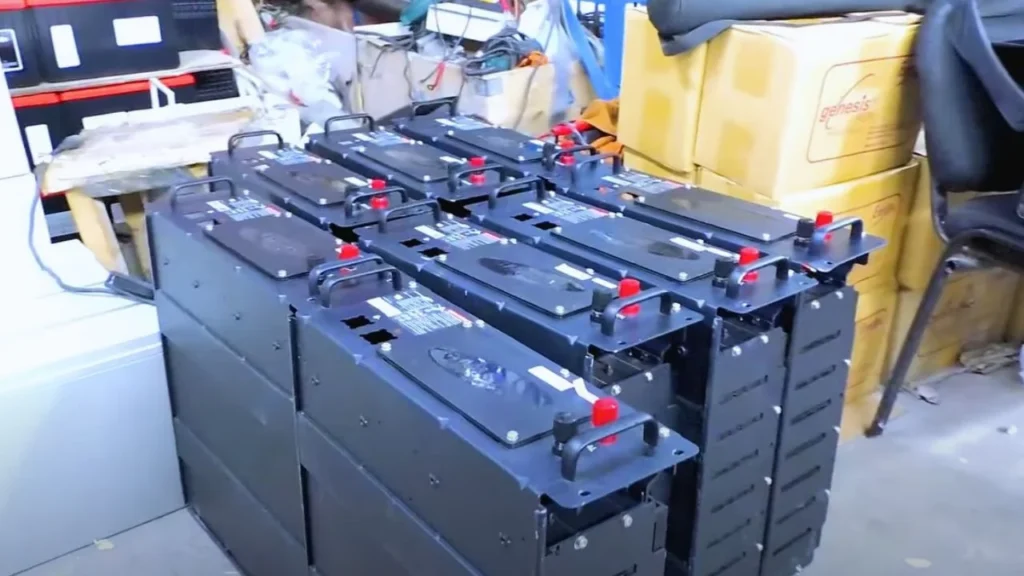

Pros:
- Longer lifespan (5-10 years)
- Higher energy density
- Lightweight and portable
- Can hold a charge for longer periods (up to 6 months without use)
Cons:
- More expensive than lead-acid models
- Sensitive to temperature fluctuations
2. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are typically found in older or budget jump starters. While they are more affordable, they come with several drawbacks compared to lithium-ion batteries. Lead-acid batteries tend to degrade faster, and they are heavier and bulkier.
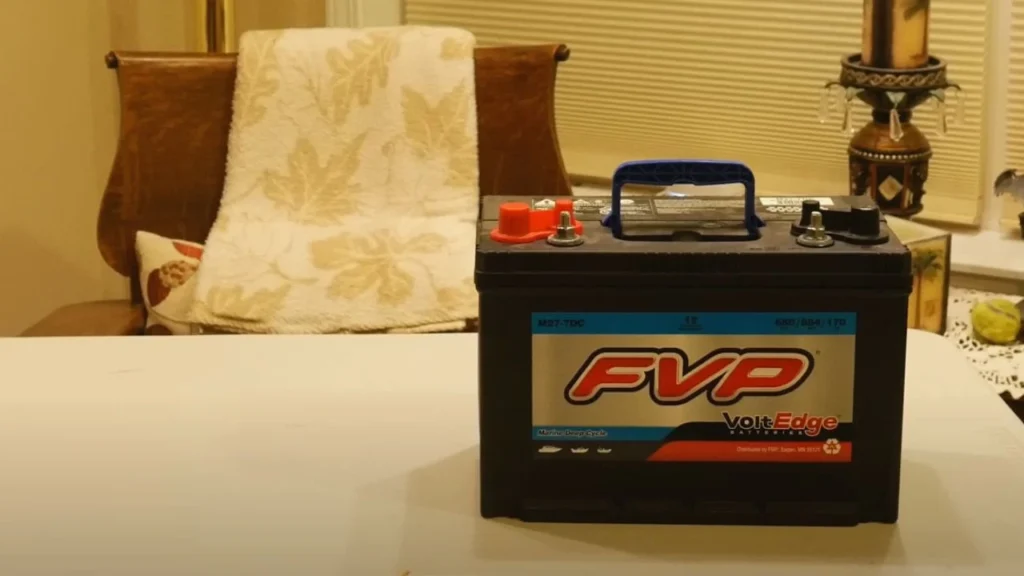

Pros:
- Less expensive
- Suitable for heavy-duty jump-starting
Cons:
- Shorter lifespan (3-5 years)
- Heavier and bulkier
- Less efficient charging and discharge cycles
Common Issues That Shorten Jump Starter Lifespan
Several avoidable mistakes can shorten the lifespan of a jump starter:
- Overcharging Even though many modern jump starters include overcharge protection, leaving the device plugged in continuously can degrade the battery over time. It’s best to unplug the jump starter once it reaches 100%.
- Full Discharge Letting the battery fully discharge regularly can also significantly reduce its capacity. Batteries that are frequently run down to 0% will degrade much faster than those recharged before reaching critical levels.
- Prolonged Exposure to Extreme Temperatures Jump starters should not be left in extreme heat (above 90°F) or freezing temperatures (below 32°F). Both high and low temperatures can cause permanent damage to the internal battery, reducing its lifespan.
- Improper Storage Storing a jump starter in a place where it is likely to get knocked around or exposed to moisture can also degrade the internal components, leading to reduced performance over time.
- Frequent Short Trips For vehicle owners, frequent short trips can impact both the vehicle’s battery and the jump starter. When the alternator doesn’t have enough time to recharge the battery fully after each use, it puts additional strain on the jump starter when it is needed. Explore the best portable marine battery jump starters for reliable performance when you’re out on the water.
How to Maximize the Lifespan of Your Jump Starter
Here are a few tips to ensure your jump starter lasts as long as possible:
- Regular Charging: Charge your jump starter every 3 to 6 months, even if you haven’t used it. This ensures the battery remains in peak condition and doesn’t suffer from deep discharges.
- Temperature Control: Store your jump starter in environments that are neither too hot nor too cold. Keeping it within the 50°F to 90°F range helps protect the battery from degradation.
- Avoid Overuse: If your vehicle doesn’t start after 3 attempts, there may be an issue with the battery or alternator that a jump starter cannot fix. Continuously trying to jump-start the car repeatedly could cause unnecessary strain on your jump starter. If your car doesn’t start after 3 attempts, the issue may lie with the battery or alternator, requiring professional attention.
- Keep Charge Levels Above 20%: Avoid letting your jump starter battery drop below 20% before recharging it. Low battery levels increase the likelihood of deep discharges, which can drastically shorten the battery’s lifespan.
- Use a Charge Controller: Many modern jump starters come with charge controllers that prevent overcharging and undercharging. These systems regulate the charging process, ensuring the battery remains within the optimal charge range.
How Often Should You Replace a Jump Starter?
Even with optimal care, no battery lasts forever. After 300-500 charge cycles or around 3-6 years of regular use, it’s time to assess the performance of your jump starter. If you notice a significant reduction in its capacity or if it struggles to jump-start your vehicle, it may be time for a replacement.
However, the exact timeline can vary depending on how well you maintain your jump starter, how frequently it’s used, and the conditions it’s exposed to. For instance, a jump starter that’s used sparingly and stored properly can last 6-10 years, while one that’s exposed to harsh environments may last closer to 3 years. Find out which portable car jump starter with air compressor is perfect for emergency roadside assistance.
How to Tell if Your Jump Starter Needs Replacement?
Here are some signs that it may be time to replace your jump starter:
- Inability to Hold a Charge: If your jump starter doesn’t hold a charge for more than a few days or loses power quickly, the internal battery may be nearing the end of its life.
- Reduced Starting Power: If it takes longer for your jump starter to crank your vehicle, or if it fails to start your car altogether, the battery’s capacity may have degraded.
- Physical Damage: If your jump starter has visible damage, such as cracked housing or damaged connectors, it may no longer be safe to use. Physical damage can compromise the device’s safety and performance.
- Slow Charging: If it takes significantly longer than usual to recharge your jump starter, it may be an indication that the battery is no longer functioning optimally.
Wrapping Up!
In conclusion, a jump starter can last anywhere from 3 to 10 years, depending on factors like battery type, usage frequency, and maintenance habits. Lithium-ion batteries tend to last longer, offering around 300-500 charge cycles and up to 10 years of use, while lead-acid batteries may last between 3-5 years under similar conditions. This comprehensive guide on using a jump starter to charge a dead battery explains whether it’s possible and what to watch out for.
Proper storage, regular charging, avoiding deep discharges, and keeping the device away from extreme temperatures are all critical factors that can help maximize the lifespan of your jump starter. By following these best practices, you can ensure your jump starter remains a reliable tool for emergency situations for many years to come. Hope so, now you know how long do jump starters last.
Ali is a tech enthusiast and automotive aficionado, passionate about sharing insights on the latest innovations and industry trends.





